Defibrillation electrode can be classified into training electrodes (for teaching purposes) and clinical AED electrode (for medical use) based on their applications. There are significant differences between the two in terms of design, function and application scenarios 。
一 . Defibrillation electrodes for training
1. Classification and Characteristics
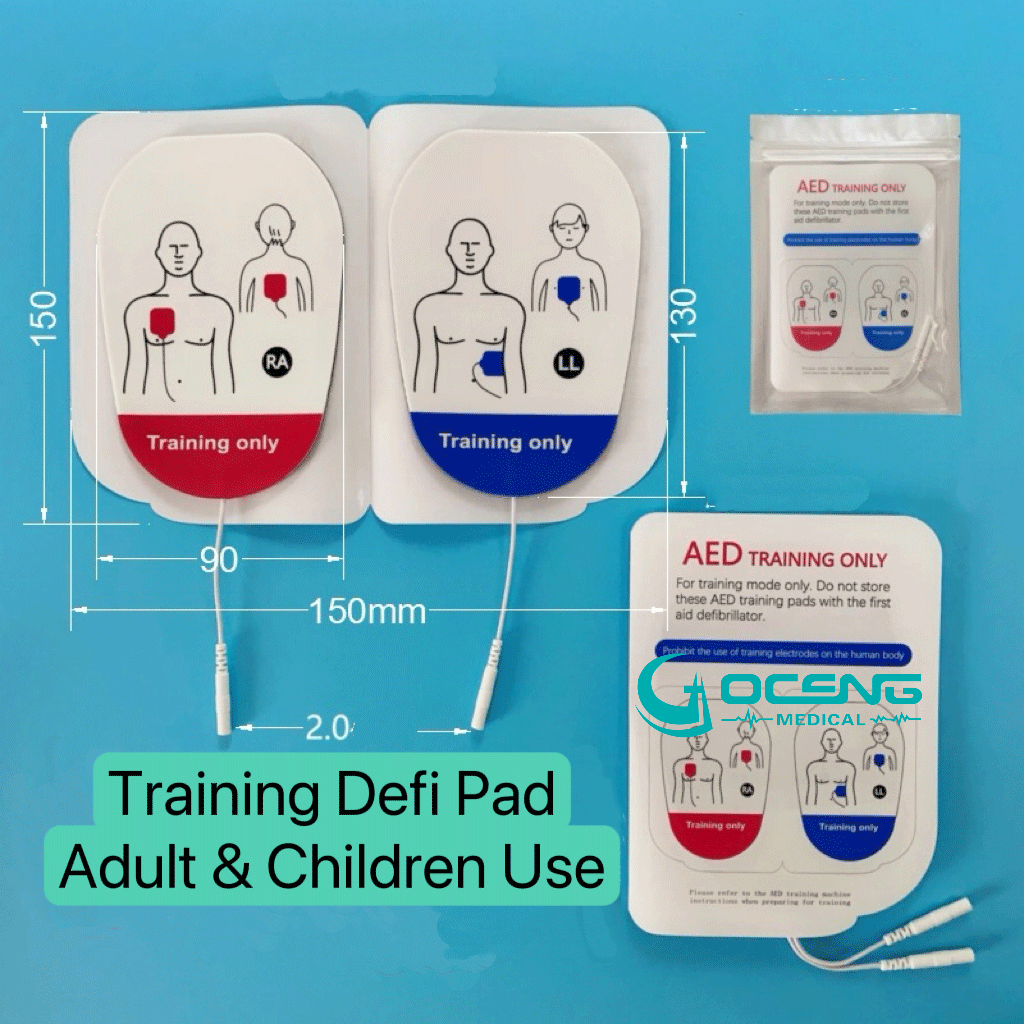
Training AED Electrode
Characteristics : The appearance is similar to that of clinical electrode, but it has no actual conductive function and is usually marked with the words "Training Only".
Application: Train the model in conjunction with an AED to simulate the real defibrillation process without electric shock output.
Application environment: First aid training courses, schools, enterprise emergency drills, etc.
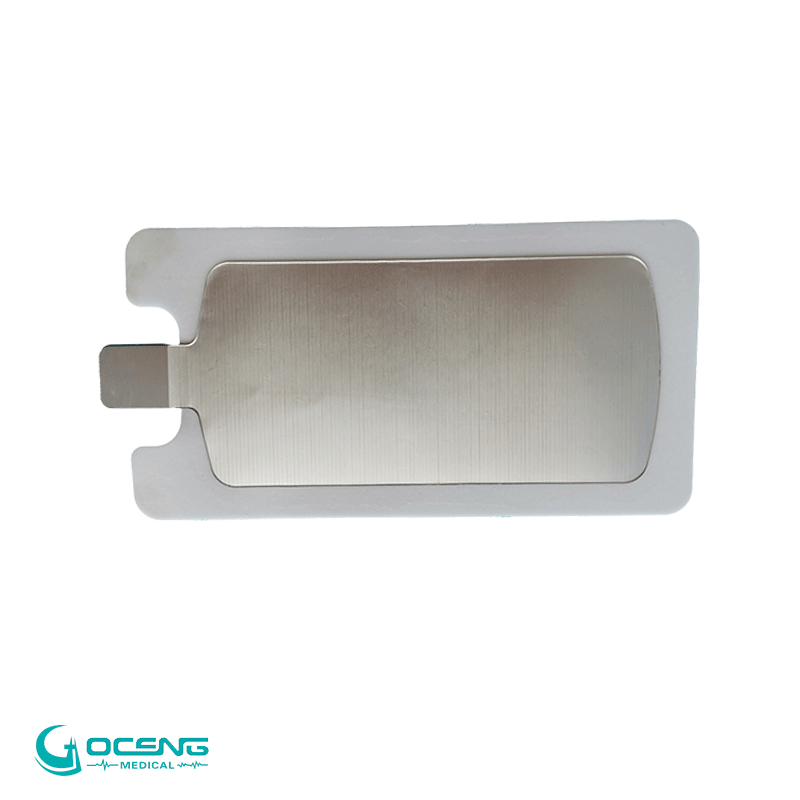
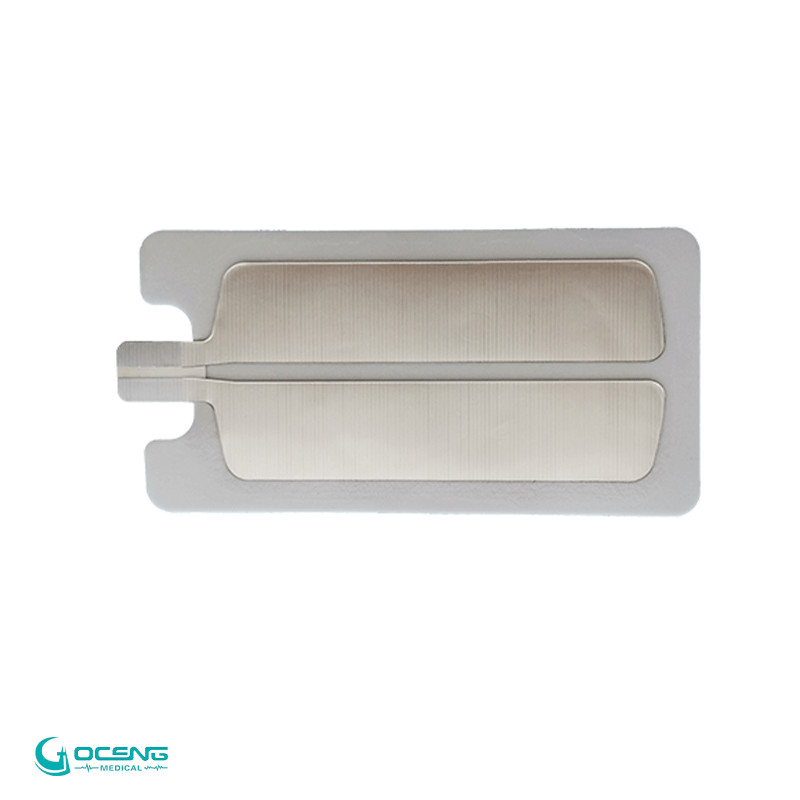
Reusable electrode plates (manual defibrillation training)
Features : Made of metal or plastic, no conductive gel, and requires connection to a defibrillator for training.
Purpose : To practice electrode placement techniques, pressing force and operation procedures.
2. Core differences
No actual electric shock function : Only for simulation to avoid the risk of false discharge.
Low cost : Reusable without the need for disinfection or gel replacement.
Clear marking : usually blue or marked with "Training" to avoid confusion.
二 . Defibrillation electrodes for clinical use
1. Classification and Characteristics
(1) By electrode form
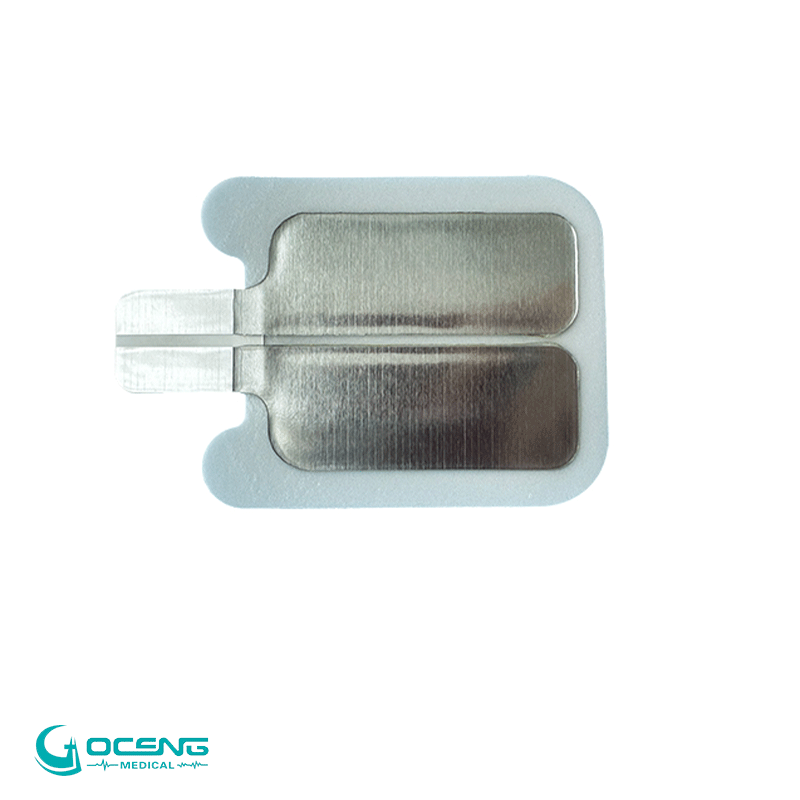
Manual defibrillation electrode pad
Features: Made of metal, it requires the application of conductive paste or the use of conductive pads, and is held and pressed by the operator.
Applicable scenarios: Professional defibrillation in hospitals (such as icus and operating rooms), where energy and timing need to be manually controlled.
Self-adhesive electrode pad (disposable)
Features: Pre-coated with conductive gel, no need to press after application, compatible with AEDs and manual defibrillators.
Advantages: Reduces the risk of operator exposure, suitable for emergency rescue sites and non-professionals (such as AEDs in public places).
(2) By patient type
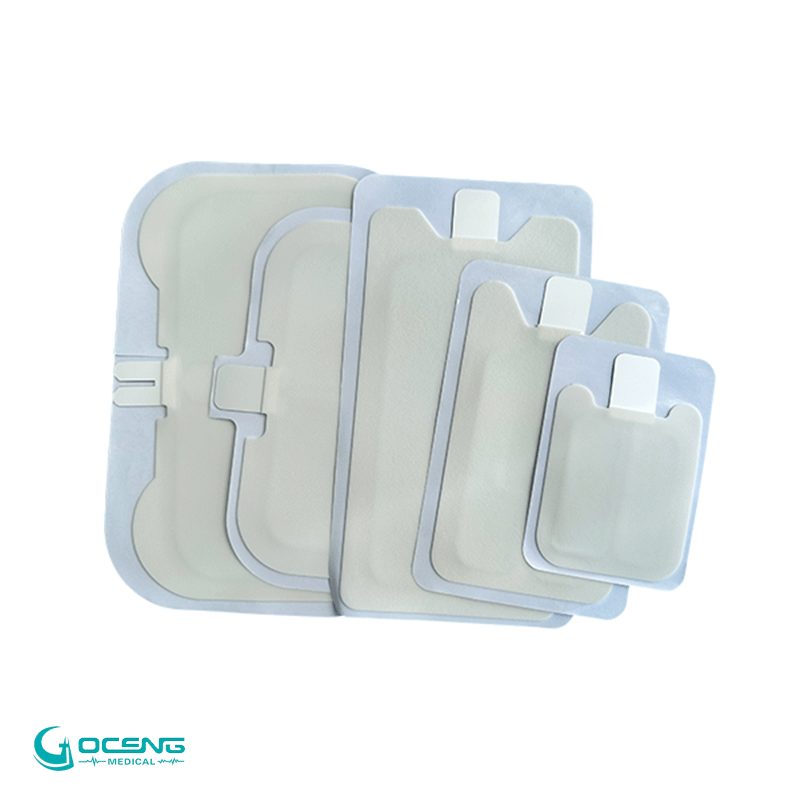
Adult's electrode : Diameter 8-12cm, energy range 50-360J.
Children's electrode: Diameter 4-8cm, energy adjustable to below 50J (Some AEDs require a dedicated children's electrode).
(3) By technical type
Single-phase wave electrode: Traditional technology, which requires relatively high energy (such as 360J), has gradually been phased out.
Biphasic wave electrode : The modern mainstream, with lower energy (120-200J), better therapeutic effect and less damage.
2. Core Features:
High conductivity requirement : It is necessary to ensure that the current is effectively transmitted to the heart.
Disposable or strict disinfection: Clinical electrodes should avoid cross-infection (self-adhesive for single use, metal plates need to be disinfected).
Safety certification: It must pass medical device certification (such as FDA, CE).
三、Note
1.Do not mix: The training electrode must not be used for real rescue, otherwise it may lead to ineffective electric shock.
2. Clinical electrode management: Checking the validity period (especially the spare electrode of AED). When storing, avoid high temperatures or humidity that may cause the gel to dry up.
3. Training authenticity: Some advanced simulators are compatible with clinical electrodes, but the electric shock function needs to be turned off.
四、Special type
Multifunctional electrode: The electrodes of a few defibrillators (such as ZOLL AED Plus) can be used for both training and clinical practice simultaneously, but this needs to be achieved through mode switching.
ICD/Pacemaker compatible electrodes: Clinical electrodes should be kept away from the implanted device area to avoid interference.
Correctly distinguishing between the two types of electrodes is the basis for ensuring teaching safety and rescue effectiveness, and the usage norms must be strictly followed. Goceng medical supports customized the training AED electrode and medicla use AED electrode by different plug wires .
Check more at : www.gocengmed.com